Human trafficking is a terrifying and very real issue that affects millions of people worldwide—it operates in secret, taking away people’s freedom and forcing them into harmful situations. This dark trade uses tricks and force to target the helpless, and it can happen anywhere.
Being aware and educated is the best protection against human trafficking, and this guide aims to explain what human trafficking looks like and how it works. More so, it will provide helpful tips and steps to keep yourself and those you care about safe from harm.
Knowing about human trafficking, spotting warning signs, and being prepared are key to staying safe. As you read on, we hope the information provided will inspire you to take action, becoming more alert and ready to stand against human trafficking.
What Is Human Trafficking?
Human Trafficking (HT), often referred to as modern-day slavery, is a grave and pervasive crime that thrives in every corner of the globe. It is an illicit trade of human beings who are subjected to involuntary servitude, sexual exploitation, and forced labor. Despite international condemnation and legal prohibitions, human trafficking continues to be a multi-billion-dollar criminal industry.
At its core, human trafficking involves the exploitation of people through force, coercion, or deceit. Traffickers prey on the vulnerable, exploiting their circumstances to gain complete control over them. The victims, stripped of their autonomy and freedom, are treated as mere commodities to be bought, sold, and exploited.
- Sex Trafficking – Sex trafficking is one of the most recognized forms of human trafficking, where individuals are forced into sexual exploitation. Victims are made to work in brothels, escort services, or pornography production against their will, with traffickers reaping the financial benefits.
- Labor Trafficking – Labor trafficking is another prevalent form, where individuals are compelled to work under exploitative conditions, often in industries like agriculture, construction, domestic work, and manufacturing. Here, traffickers employ coercion, threats, and physical restraint to ensure compliance from their victims.
- Child Trafficking – Children are particularly vulnerable to trafficking, be it for forced labor, sexual exploitation, or use in child soldiering. Traffickers exploit the innocence and helplessness of children for various nefarious purposes.
- Forced Marriage – Forced marriage is a form of trafficking where individuals, usually women and girls, are forced into marriages without their consent. Here, too, coercion, violence, and deceit are used to achieve compliance.
- Organ Trafficking – Organ trafficking involves the illicit trade of organs, where victims are either deceived or forced to give up their organs, which are then sold on the black market.
- Debt Bondage – Debt bondage is a form of human trafficking where individuals are forced to work to pay off a debt, with terms and conditions that are often impossible to meet, trapping the victims in a cycle of endless labor.
Each form of human trafficking is heinous and devastates the lives of victims, often leaving them with lifelong scars. Understanding the various faces of human trafficking is a crucial step toward combating it and preventing further victimization.
How Prevalent Is Human Trafficking?
Human trafficking remains a persisting and alarming issue across the globe, with its nefarious ripples touching every region. The intricacies of this illicit trade span across various forms, making it a complex problem to tackle. Despite concerted efforts by nations and international bodies, human trafficking continues to thrive, leaving a trail of devastated lives in its wake. The statistics about this crime elucidate the magnitude of the challenge the world faces in eradicating human trafficking.
Global Prevalence
The most recent data from the United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC) unveils a concerning picture of human trafficking worldwide. Their report covering 141 countries highlights that the number of detected trafficking victims globally fell by 11% in 2020 compared to the previous year. This decline was particularly noted in low- and medium-income countries, possibly due to the pandemic, which may have hampered law enforcement capacities to detect and report cases of trafficking.
The global conviction rates for trafficking offenses also plummeted by 27% in 2020 from the year before, with notable decreases observed in South Asia (56%), Central America and the Caribbean (54%), and South America (46%).
Victim Identification
The UNODC report also delves into the distressing trend of self-rescue among trafficking victims, where more victims are escaping and reporting to authorities on their own (41%) as compared to those located by law enforcement (28%). This is alarming as many victims may not identify themselves as victims or may be too fearful to attempt to escape from their exploiters.
Impact of Conflicts and Crises
War and conflicts exacerbate the risks of human trafficking, with the displaced populations being particularly susceptible. The ongoing war in Ukraine, for instance, has heightened trafficking risks for the displaced, with most victims from conflicts being trafficked to countries in Africa and the Middle East.
Trend Over the Years
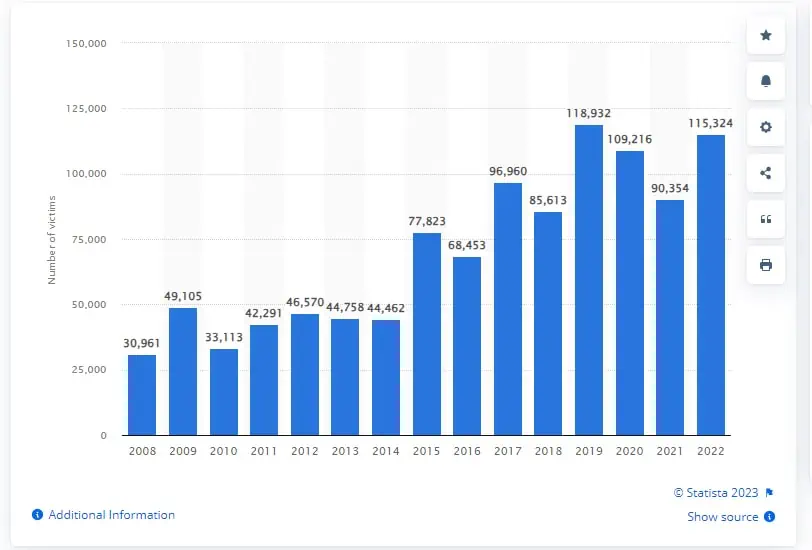
Between 2008 and 2019, the number of identified human trafficking victims worldwide soared from around 30,000 to nearly 120,000, marking a substantial increase over the years. However, the COVID-19 pandemic seems to have morphed the landscape of human trafficking, with fewer cases of trafficking for sexual exploitation detected due to public space closures and related restrictions.
Government Involvement
The 2023 Trafficking in Persons Report identifies 11 governments with a documented “policy or pattern” of human trafficking:
- Afghanistan
- Burma
- China, People’s Republic of
- Cuba
- Eritrea
- Iran
- Korea, Democratic People’s Republic of
- Russia
- South Sudan
- Syria
- Turkmenistan
Indicating involvement in trafficking in government-funded programs, forced labor in government-affiliated medical services, sexual slavery in government camps, or the employment or recruitment of child soldiers.
Continuous Monitoring and Data Collection
Continuous efforts are being made to measure and analyze the nationwide incidence of human trafficking. Reports like the one from the Bureau of Justice Statistics detail ongoing and completed efforts to describe characteristics of human trafficking victims and offenders and to describe criminal justice responses to human trafficking offenses.
How Easy Is It to Become a Victim of HT Online?
The digital era has not only simplified our lives but also eased the modus operandi of nefarious activities like human trafficking. Online platforms, especially social media and dating apps, have become fertile grounds for traffickers to scout and recruit victims. The cloak of anonymity that the internet provides, coupled with the vast reach that online platforms offer, has made online recruitment a significant aspect of modern-day human trafficking.
Online Recruitment
The Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) has cautioned the public about the risks posed by human traffickers on popular online platforms. Traffickers exploit these platforms to recruit and later advertise sex trafficking victims. Additionally, traffickers lure individuals into labor trafficking through seemingly legitimate job offers.
Methodology
Traffickers use deceitful tactics to ensnare individuals online. They pose as genuine job recruiters, agents for modeling companies, or employment agencies while hiding their true intentions. By offering better life opportunities or fake employment offers, they groom their victims online.
They exploit personal information shared on online platforms to target vulnerable individuals, especially those facing financial hardships or low self-esteem. Once a false sense of trust is established, traffickers coerce the victims to meet in person, eventually forcing them into sex work or labor trafficking.
Examples include, but are in no way limited to:
- In 2019, a man from Baltimore exploited the financial distress of two girls, who had shared their struggles online, to force them into sex work.
- A married couple from California used online platforms and an India-based newspaper to post false job advertisements, later forcing the recruited individuals into oppressive domestic labor.
- A victim from the Seattle area was promised help with her acting career by a trafficker she met on a dating website, only to be later abused and forced into prostitution.
Prevalence
While exact statistics regarding the number of individuals recruited online for trafficking purposes are hard to come by, the ease of online recruitment and numerous case studies demonstrate a significant risk. It’s believed that human trafficking is the third most prevalent criminal activity globally, and online recruitment plays a substantial role in this prevalence.
Addressing the Gap
Research initiatives, such as a global systematic review, are ongoing to understand the recruitment mechanisms better and devise effective strategies to counter online recruitment for human trafficking. Another effort to measure and analyze the nationwide incidence of human trafficking, including online recruitment, is seen in the data collection activities reported in 2023.
The amalgamation of the vast reach of online platforms, the anonymity they offer, and the desperation of vulnerable individuals creates a conducive environment for online recruitment in human trafficking. Continuous efforts to educate the public, create safer online spaces, and enhance legal frameworks are imperative to combat this modern-day slavery extension.
How Do Traffickers Recruit?
Human traffickers have honed their recruitment techniques to exploit the vulnerable effectively. The rise of the internet has only expanded its toolkit, providing a vast and often anonymous platform to lure potential victims. Below are some common online recruitment strategies traffickers employ, according to NordVPN:
Catfishing
Traffickers often create fake profiles on social media or dating apps to initiate contact with potential victims. By building a relationship online, they gain the trust of the victim, which they later exploit to entrap them into trafficking. They use fake photos, fabricated stories, and charming personalities to make their prey fall for them. Once a rapport is established, they persuade the victim to meet in person, which is where the entrapment occurs. This tactic is particularly dangerous for children, who are more susceptible to such deceit.

Cyberstalking
Oversharing on social media platforms can lead to cyberstalking by traffickers. They utilize location check-ins on Facebook and geotags on Instagram pictures to track the daily routine and whereabouts of potential victims. This information helps traffickers determine when and where a person is most likely to be alone, making it easier to approach and abduct them.

Phishing
Traffickers also employ phishing tactics, similar to cybercriminals, to gather personal information or track the location of potential victims. They may send messages with malicious links that, when clicked, reveal the victim’s location or install malware on their devices to gather more information. Many people fall for these scams and unknowingly expose themselves to the risk of trafficking.

Seeking Those Feeling Misunderstood or Unhappy
Research from the University of Toledo studied the nature of social media posts that point the interest of traffickers toward potential victims. When individuals express feelings of being misunderstood, discontentment with their single status, or concerns about their appearance on social platforms, they might inadvertently attract traffickers. Traffickers often capitalize on these sentiments by responding with empathetic statements like “I understand you” to initiate conversations.
The interactive nature of social media, particularly the chat functionality, affords traffickers the luxury of time to dissect the worries of individuals and tailor their responses to entrap them effectively. Unlike the pre-internet era, when traffickers engaging in in-person recruitment had only a brief window to gauge and exploit a person’s vulnerabilities, online chats provide a longer interaction period. This extended communication timeframe facilitates a trust-building process between the victim and the trafficker.
Furthermore, the University of Toledo’s investigation unveiled that 42% of victims who interacted with traffickers online never met them face-to-face, yet they were trafficked. This finding illuminates the extensive and networked structure underpinning many sex trafficking operations, underscoring the perilous potential of online interactions with malevolent actors.
Most Common Signs of Recruitment?
Vigilance is a crucial tool in combating human trafficking, especially in the digital realm, where traffickers deploy a myriad of deceptive tactics. Being aware of the common signs of recruitment can significantly aid in identifying and averting potential trafficking attempts. Here are some “red flags” to watch for when using online platforms:
Too Good to Be True Offers
- Job offers with exceptionally high pay, minimal experience requirements, or promises of quick promotions.
- Invitations to exclusive events or parties, especially if you’re offered free transportation and accommodation.
Vagueness and Inconsistencies
- Lack of clear information or inconsistent details about the job, event, or person contacting you.
- Unwillingness to provide verifiable information or evade direct questions.
High Pressure Tactics
- Urgency in decision-making, like insisting on immediate replies or commitments.
- Pressure to share personal information or photographs.
Unprofessional Communication
- Poorly written messages, inconsistent formatting, or unprofessional language.
- Communications solely through messaging apps, personal emails, or texts, avoiding official channels.
Requests for Money
- Being asked to pay for training, uniforms, or other fees as a condition of employment.
- Requests for financial help or personal bank information.
Isolation from Personal Networks
- Encouragement to cut ties with friends or family or to keep interactions a secret.
- Pushing for in-person meetings in secluded or unusual locations.
Exploitation of Personal Circumstances
- Targeting individuals going through financial hardships, personal struggles, or desperate situations.
- Offering unsolicited help or too much attention to personal problems.
Unsolicited Contacts
- Receiving unsolicited job offers, invitations, or friend requests from unknown individuals or accounts with minimal activity.
- Persistent and unwelcome communications even after expressing disinterest.
Privacy Invasion
- Unwanted sharing or requesting of intimate images or information.
- Attempts to gather extensive personal information without a legitimate reason.
Check for Reviews and Verification
- Look for reviews or verification badges on profiles and companies.
- Verify the legitimacy of the offer or individual through independent sources or official channels.
Being equipped with the knowledge of these red flags and maintaining a cautious approach when interacting online can go a long way in preventing oneself and others from falling prey to human traffickers.
How You Can Protect Yourself from Becoming a Victim?
Staying safe online is crucial to avoid dangerous situations like human trafficking. Here are some simpler tips to help protect yourself:
- Be Cautious: Don’t trust everything you see online, especially if it seems too good to be true.
- Verify People: If someone new contacts you online, verify who they are. Look for inconsistencies in what they tell you.
- Don’t Share Too Much: Avoid posting personal details, location, or your daily routines on social media.
- Know About Catfishing: Catfishing is when someone creates a fake profile to trick you. Be cautious with new online relationships.
- Avoid Phishing Scams: Don’t click on suspicious links in emails or messages, as they might be scams to gather your information.
- Keep Profiles Private: Use privacy settings on social media, and be careful about who you add as friends.
- Learn the Signs: Know the common tricks traffickers use, like fake job offers or promises.
- Trust Your Gut: If something feels wrong, trust your feelings and step away from the situation.
- Ask for Help: If you think you’re being targeted, contact local law enforcement or organizations that fight human trafficking.
- Stay Updated: Keep learning about the latest scams and trafficker tricks to stay safe.
What to Do if You Suspect You or Someone You Know Is in Danger
Recognizing the signs of human trafficking and taking immediate action is crucial to ensure the safety of oneself or others. Here are steps to follow if you suspect danger, along with a list of signs indicative of trafficking:
Signs of Trafficking
- Unusual working hours or living conditions.
- Signs of physical abuse or fear.
- Lack of personal possessions or identification documents.
- Avoidance of eye contact, social interaction, or authority figures.
- Inconsistent stories or scripted responses.
- Overly controlling or abusive employer or partner.
Document Evidence
- Keep a record of any suspicious conversations, messages, or encounters.
- Take screenshots and note dates, times, and details of the incidents.
Do Not Confront the Suspected Trafficker
- Confronting the trafficker could endanger you or the victim further. Leave interventions to the professionals.
Contact Law Enforcement
- If it’s an emergency, call 911 or your local emergency number.
- For non-emergencies, contact local law enforcement to report your suspicions.
Reach Out to Helplines
- Call the National Human Trafficking Hotline at 1-888-373-7888 or text “HELP” to 233733.
- Contact local or national anti-trafficking organizations for guidance and support.
Be Prepared to Provide Information
- Have the details ready when contacting authorities. The more information you can provide, the better.
Educate Yourself and Others
- Knowledge is power. Learn about human trafficking, share information, and promote awareness in your community.
Stay Connected
- Keep lines of communication open with those you are concerned about and check in on their well-being regularly.
Frequently Asked Questions
The sinister world of human trafficking can leave people with a lot of questions about its operations, the extent of its reach, and the measures one can take for protection. This FAQ addresses some common issues concerning human trafficking, its online manifestation, and the preventative steps people can take to safeguard themselves and their communities.
What Is Human Trafficking, and How Does It Happen Online?
Human trafficking is a criminal activity involving the exploitation of individuals through force, coercion, or deceit. Online traffickers use social media, dating apps, and other platforms to recruit and exploit victims by building trust through fake profiles, false job offers, and deceptive relationships.
How Widespread Is Human Trafficking Today?
Human trafficking continues to be a significant global issue, with cases reported in numerous countries. The exact prevalence can be challenging due to its clandestine nature, but continuous efforts are made to identify and assist victims.
What Are Some Red Flags of Online Recruitment by Traffickers?
Red flags include too-good-to-be-true job offers, high-pressure tactics, requests for money, unsolicited contacts, and vague or inconsistent information.
How Do Traffickers Lure People Online?
Traffickers often use catfishing, phishing, and cyberstalking to deceive individuals. They create fake profiles, send malicious links, or track personal information shared online to target potential victims.
How Can I Protect Myself from Online Recruitment?
Some protective measures include being skeptical, verifying identities, avoiding oversharing personal information, understanding common trafficker tactics like catfishing and phishing, and maintaining a private and secure online presence.
What Should I Do if I Suspect Someone Is Being Trafficked?
Document any suspicious activity, avoid confronting the suspected trafficker, contact law enforcement, reach out to helplines, and support the suspected victim while maintaining your own privacy.
What Are the Common Signs Someone Might Be a Victim of Human Trafficking?
Signs may include unusual working hours, signs of physical abuse, lack of personal possessions, avoidance of social interaction, and overly controlling or abusive relationships.
Can Human Trafficking Happen without In-Real-Life Contact?
Yes, some victims are trafficked purely online, for instance, through coercion into pornography or other exploitative situations without meeting the trafficker in person.
How Are Authorities and Organizations Working to Combat Human Trafficking?
Authorities and organizations are engaging in victim identification, public awareness campaigns, legal enforcement, data collection, and analysis to understand and combat human trafficking better.
Where Can I Learn More or Report the Suspicions of Human Trafficking?
The National Human Trafficking Hotline (1-888-373-7888) is a resource for reporting suspicions or seeking help. Additionally, local law enforcement agencies, anti-trafficking organizations, and reputable online resources are avenues to learn more and report concerns.